Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Physics and Electronics, Hunan University, Changsha 410082, China
2 College of Traffic Engineering, Hunan University of Technology, Zhuzhou 412007, China
3 College of Electrical and Information Engineering, Hunan University, Changsha 410082, China
In this article, we investigate the phenomenon of coherent perfect absorption (CPA) with bulk Dirac semimetal (BDS) thin film. CPA of BDS appears at the frequency of 43.89 THz with 0° phase modulation of two coherent input lights. Meanwhile, it shows that CPA can be realized under oblique incidence circumstances for both TM and TE polarizations. Moreover, the frequency of CPA can be adjusted by altering the thickness of BDS thin film, and the dynamic regulation of CPA can be realized by changing the Fermi energy. Finally, the peak coherent absorption frequency can be controlled by changing the degeneracy factor.
coherent perfect absorption bulk Dirac semimetal thin film phase modulation Chinese Optics Letters
2021, 19(8): 081601
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Physics and Electronics, Hunan Normal University, Changsha 410081, China
2 International Collaborative Laboratory of 2D Materials for Optoelectronic Science & Technology of Ministry of Education, College of Optoelectronic Engineering, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
The optical Tamm state (OTS), which exists generally at the interface between metal and a dielectric Bragg mirror, has been studied extensively in the visible and near infrared spectra. Nevertheless, OTS in the terahertz (THz) region normally receives far less attention. In this Letter, we demonstrate the physical mechanism of OTS at the interface between graphene and a dielectric Bragg mirror in the THz frequency band by applying the transfer matrix method and dispersion characteristics. Based on such mechanisms, we propose an efficient method that can precisely generate and control OTS at a desired angle and frequency. Moreover, we show that the OTS is dependent on the optical conductivity of graphene, making the graphene–dielectric-Bragg-mirror a good candidate for dynamic tunable OTS device in the THz frequency range.
160.4236 Nanomaterials Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(2): 020008

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 SZU-NUS Collaborative Center and International Collaborative Laboratory of 2D Materials for Optoelectronic Science & Technology of Ministry of Education, College of Optoelectronic Engineering, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
2 Engineering Technology Research Center for 2D Material Information Function Devices and Systems of Guangdong Province, College of Optoelectronic Engineering, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
As a kind of two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenide material, tungsten diselenide (WSe2) has attracted increasing attention, owing to its gapped electronic structure, relatively high carrier mobility, and valley pseudospin, all of which show its valuable nonlinear optical properties. There are few studies on the nonlinear optical properties of WSe2 and correlation with its electronic structure. In this paper, the effects of spatial self-phase modulation (SSPM) and distortion influence of WSe2 ethanol suspensions are systematically studied, namely, the nonlinear refractive index and third-order nonlinear optical effect. We obtained the WSe2 dispersions SSPM distortion formation mechanism, and through it, we calculated the nonlinear refractive index n2, nonlinear susceptibility χ(3), and their wavelength dependence under the excitation of 457 nm, 532 nm, and 671 nm lasers. Moreover, by use of its strong and broadband nonlinear optical response, all-optical switching of two different laser beams due to spatial cross-phase modulation has been realized experimentally. Our results are useful for future optical devices, such as all-optical switching and all-optical information conversion.
Photonics Research
2018, 6(11): 11001040

Author Affiliations
Abstract
SZU-NUS Collaborative Innovation Center for Optoelectronic Science & Technology, Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Devices and Systems of Ministry of Education and Guangdong Province, College of Optoelectronic Engineering, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
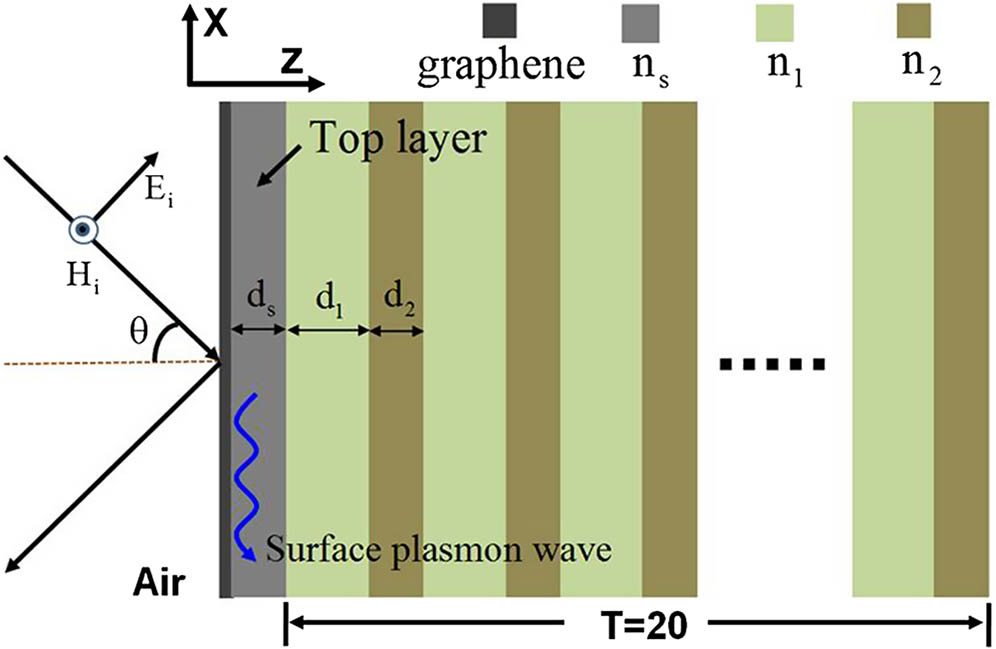
In this paper, we have shown that perfect absorption at terahertz frequencies can be achieved by using a composite structure where graphene is coated on one-dimensional photonic crystal (1DPC) separated by a dielectric. Due to the excitation of optical Tamm states (OTSs) at the interface between the graphene and 1DPC, a strong absorption phenomenon occurs induced by the coupling of the incident light and OTSs. Although the perfect absorption produced by a metal–distributed Bragg reflector structure has been researched extensively, it is generally at a fixed frequency and not tunable. Here, we show that the perfect absorption at terahertz frequency not only can be tuned to different frequencies but also exhibits a high absorption over a wide angle range. In addition, the absorption of the proposed structure is insensitive to the polarization, and multichannel absorption can be realized by controlling the thickness of the top layer.
(240.6680) Surface plasmons (350.2450) Filters absorption (040.2235) Far infrared or terahertz. Photonics Research
2017, 5(6): 06000536

Author Affiliations
Abstract
SZU-NUS Collaborative Innovation Center for Optoelectronic Science & Technology, Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Devices and Systems of Ministry of Education and Guangdong Province, College of Optoelectronic Engineering, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
The photonic spin Hall effect (SHE) has been intensively studied and widely applied, especially in spin photonics. However, the SHE is weak and is difficult to detect directly. In this paper, we propose a method to enhance SHE with the guided-wave surface-plasmon resonance (SPR). By covering a dielectric with high refractive index on the surface of silver film, the photonic SHE can be greatly enhanced, and a giant transverse shift of horizontal polarization state is observed due to the evanescent field enhancement near the interface at the top dielectric layer and air. The maximum transverse shift of the horizontal polarization state with 11.5 μm is obtained when the thickness of Si film is optimum. There is at least an order of magnitude enhancement in contrast with the transverse shift in the conventional SPR configuration. Our research is important for providing an effective way to improve the photonic SHE and may offer the opportunity to characterize the parameters of the dielectric layer with the help of weak measurements and development of sensors based on the photonic SHE.
(240.0240) Optics at surfaces (260.6970) Total internal reflection (310.2785) Guided wave applications. Photonics Research
2017, 5(5): 05000467

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 SZU-NUS Collaborative Innovation Center for Optoelectronic Science & Technology, Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Devices and Systems of Ministry of Education and Guangdong Province, College of Optoelectronic Engineering, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
2 College of Physics and Energy, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
An ultrasensitive biosensor based on hybrid structure and composed of long-range surface plasmon polariton (LRSPP) and dielectric planar waveguide (PWG) modes is proposed. Both PWG and LRSPP modes have strong resonances to form strong coupling between the two modes, and the two modes can couple to enhance sensitivityof sensors. In the hybrid structure, PWG is composed of cytop–Si–cytop multilayers and the LRSPP configuration is composed of cytop–metal–sensing medium multilayer slabs. The highest imaging sensitivities of 2264 and 3619 RIU?1 were realized in the proposed sensors based on Au and Al-monolayer graphene, respectively, which are nearly 1.2 and 1.9 times larger than the 1910 RIU?1 sensitivity of the conventional LRSPR sensor (LRSPP sensor). Moreover, it is demonstrated that the PWG-coupled LRSPP biosensor is applicable to the sensing medium, with refractive index in the vicinity of 1.34.of Guangdong Province (2016B050501005); Science and Technology Project of Shenzhen (JCYJ20140828163633996, JCYJ20150324141711667); Natural Science Foundation ofSZU (201452, 201517, 827-000051, 827-000052, 827-000059).
Remote sensing and sensors Remote sensing and sensors Sensors Sensors Remote sensing and sensors Remote sensing and sensors Biological sensing and sensors Biological sensing and sensors Optical sensing and sensors Optical sensing and sensors Surface plasmons Surface plasmons Photonics Research
2016, 4(6): 06000262
1 湖南大学信息科学与工程学院微纳光电器件及应用教育部重点实验室, 湖南 长沙 410082
2 湖南大学电气与信息工程学院, 湖南 长沙 410082
研究含负折射介质的不对称反向定向耦合器中的时空调制不稳定性(MI),探讨了输入功率、前向波和后向波功率比和通道间的耦合系数等对时空MI的影响。结果表明:在这种新型耦合器中只有当横向波数超过一定阈值时才会产生MI,增加输入功率或减少前向波和后向波的功率比都会扩大MI增益谱的范围并最终使MI区域重合,而降低耦合器通道间的耦合系数可减少MI的增益峰值但拓宽增益谱的范围。负折射介质的电磁参数可调谐特性为实现MI的主动调控和孤子的形成提供了新的方法和手段。
非线性光学 时空调制不稳定性 反向定向耦合器 负折射介质 孤子
湖南大学 计算机与通信学院微纳光电器件及应用教育部重点实验室,湖南 长沙 410082
超常材料具有人工设计的结构,并有自然材料所不具备的超常物理性质。超常材料的电磁响应灵活可调,对太赫兹(THz)技术意义非凡。THz 超常材料的实现和迅速发展为太赫兹技术的发展和应用带来了新的机遇。总结了THz波段超常材料的研究进展,包括THz波段超常材料的构造及制备、基于超常材料的THz波器件以及超常材料在THz波技术中的其他应用。
超常材料 太赫兹(THz) 负折射 光子晶体 激光与光电子学进展
2010, 47(5): 051601
湖南大学 计算机与通信学院微纳光电器件及应用教育部重点实验室,湖南 长沙 410082
基于Drude模型研究了超常介质中的色散磁导率对时空不稳定性(STI)的影响,得到了具有赝五阶非线性效应和自陡效应情形下时空不稳定性增益谱的一般表达式。结果表明,在负折射区,对于自聚焦介质,赝五阶非线性使调制增长的频谱范围和增益值增大,而对于自散焦介质,作用则相反,这与常规介质中的现象不同;在正折射区,赝五阶非线性会抑制自聚焦介质中的时空不稳定性,与常规介质中的现象相同。此外,超常介质中自陡效应可能为负值,但无论自陡效应是正或负,都能抑制时空不稳定性的产生。
非线性光学 时空不稳定性 超常介质 赝五阶非线效应 自陡
湖南大学计算机与通信学院, 湖南 长沙 410082
光与超常介质相互作用时,光的磁场也变得很重要。超常介质的色散磁导率导致光与超常介质的非线性相互作用呈现出许多新特性。总结了超常介质中二阶非线性光学现象的国内外研究进展,报道了在三阶非线性超常介质中光的传输特性方面的研究结果,包括传输模型的建立、调制不稳定性、孤子和自聚焦现象等。
非线性光学 超常介质 负折射 调制不稳定性 孤子 自聚焦 倍频 参量放大





